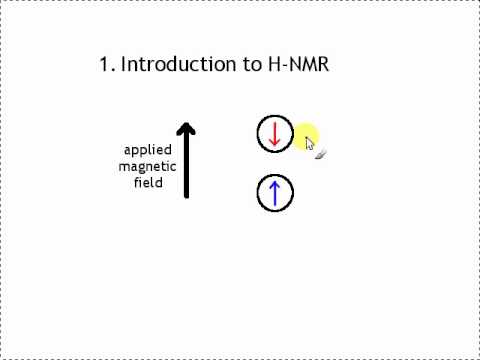
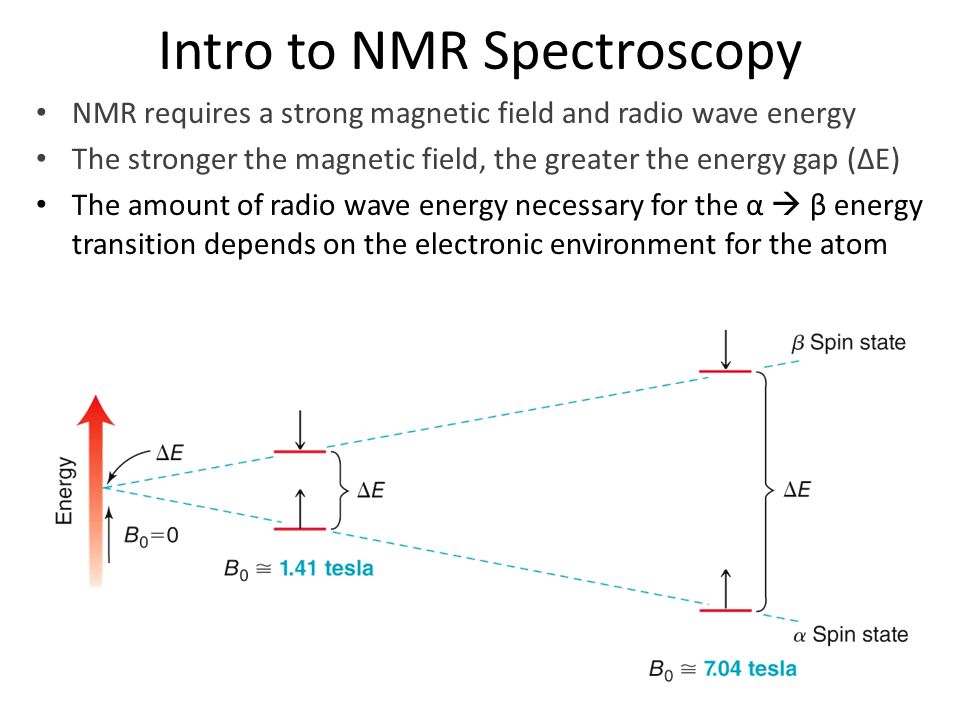
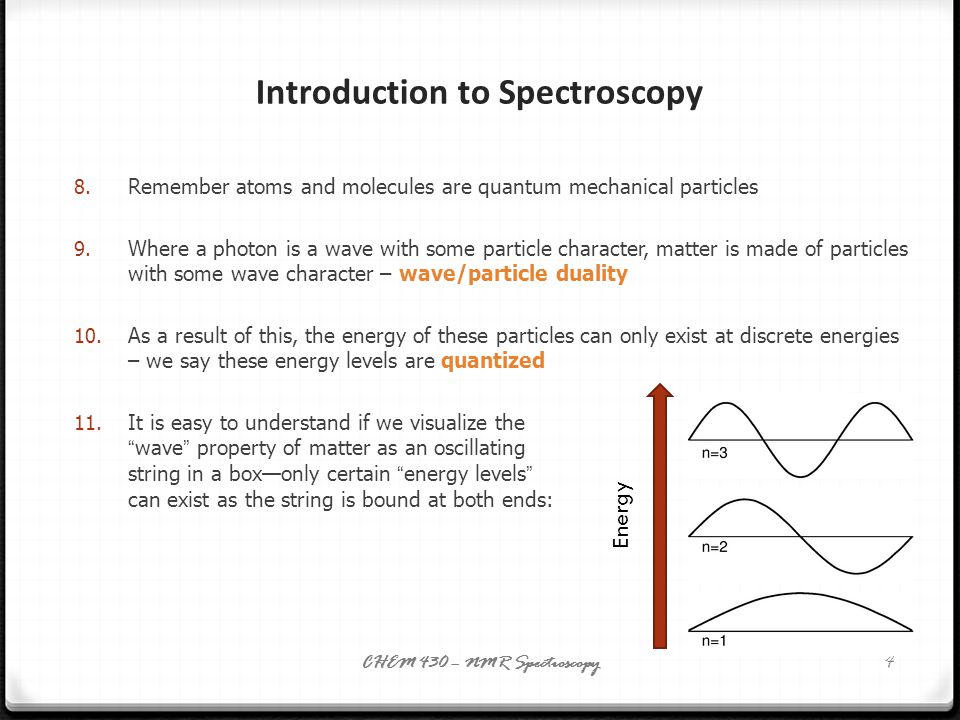
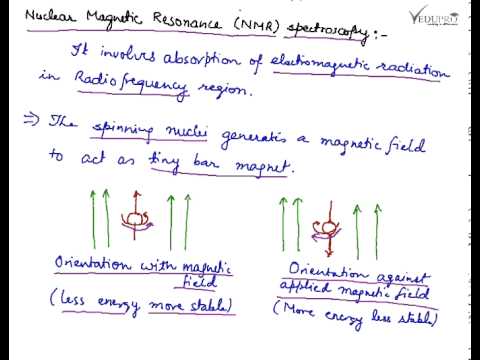
Introduction to Spectroscopy. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Absorption in the lowenergy radiofrequency part of the spectrum causes excitation of nuclear spin states. NMR spectrometers are tuned to certain nuclei (e. Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy R. Abraham, School of Chemistry, University of Liverpool J. Fisher, Biological NMR Centre, University of Leicester P. Loftus, Stuart Pharmaceuticals, Delaware, USA This book is a new, extended edition of Proton and. Spectroscopy is the study of how light interacts with matter. We can use spectroscopy to determine the structure and functional groups in organic compounds. We will be learning about how to use IR, UVVis, and NMR spectroscopy. NMR is a branch of spectroscopy and so it describes the nature of the energy levels of the material system and transitions induced between them through absorption or. Introduction to Spectroscopy and Applications. March2017 i Preface effect is used in nuclear resonance spectroscopy (NMR) and can also be used to generate the images from resonance imaging (MRI). When an electron absorbs infrared. 1 Chapter 13: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy direct observation of the Hs and Cs of a molecules Nuclei are positively charged and spin on an axis; they create a (Cavanagh, et al. Protein NMR spectroscopy) At the local position of a nuclear spin within a molecule the external field B 0 is shielded by the local electronic environment. PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (HNMR) WHAT IS HNMR SPECTROSCOPY? 2 Introduction NMR or nuclear resonance spectroscopy is a technique used to determine a compounds unique structure. It identifies the carbonhydrogen framework of an organic 1 Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy Tremendous progress has been made in NMR spectroscopy with the introduction of multidimensional NMR spectroscopy and pulse Fourier transform NMR. Introduction to spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the way light radiation) and matter interact. There are a number of different types of spectroscopic techniques and the basic principle shared by all is t 1 Introduction The first application of nuclear resonance spectroscopy (NMR, sometimes referred to as n. in oldfashioned texts) to a biological sample was reported1 in 1954 by Jacobson, Anderson, and Arnold on the effect of hydration of deoxyribonucleic acid, one E. Kwan Lecture 1: Introduction to NMR Chem 117 The Chemical Shift Now, I'll show you some spectra, and explain everything by example. Introduction to Molecular Spectroscopy University of Manchester About this course: The course introduces the three key spectroscopic methods used by chemists and biochemists to analyse the molecular and electronic structure of atoms and molecules. Theory and Applications of NMR Spectroscopy Arthur S. Edison Department of Biochemistry Molecular Biology Summary Week 1 Notes: Introduction to the basics: Bloch equations This course is an introduction to modern NMR experiments and their application to biological problems. NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for biologists interested in the structure, dynamics, and interactions of biological macromolecules. This review aims at presenting in an accessible manner the requirements and limitations of this technique. As an introduction, the history of NMR will highlight. Introductory to NMR Spectroscopy References: 1. NMR Spectroscopy, n Biological application become possible due to the introduction superconducting n NMR imaging was demonstrated. NMR is a versatile tool and it has applications in wide varietie s of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful and theoretically complex analytical tool. Basic 1H and 13CNMR Spectroscopy provides an introduction to the principles and applications of NMR spectroscopy. videos Play all Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Part 1 15: 33. Basics and principle of Raman Spectroscopy Introduction to Infrared Spectroscopy. Organic chemistry: Introduction to proton NMR (nuclear resonance) spectroscopy. nonequivalent hydrogens; chemical shift; integration; spinspin splitting. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy has become the dominant method of analysis for organic compounds, because in many cases it provides a way to determine an entire structure using one set of analytical tests. Introduction to NMR Part 1 Revised Anne M. Niobiumtincopper clad coil wound like a spool of thread. The current runs through this coil, creating the field. BIOMOLECULAR NMR SPECTROSCOPY, Oxford Press, 1995 Varian Associates, Inc. A Complete Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy is written by Roger S. Macomber and published by John Wiley and Sons Inc. Now a days Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy is widely used in worldwide for structure elucidation of compoundsmolecules and this book is very useful to understand the basics of modern Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. NMR is a very powerful technique that enables the study of physicochemical, electronic, and structural properties of molecules, looking at the quantum mechanical properties of an atomic nucleus (specifically, the chemical shift and Zeeman effect on the resonant frequency), in solution as well as the solid state. Learning Guide for Chapter 5 NMR Spectroscopy I. Introduction to NMR spectroscopy p 1 II. Distinguishing equivalent H's p 3 VI. Introduction to NMR spectroscopy To introduce you to NMR spectroscopy, we will first compare it. 2D NMR Introduction Table of Contents 1. Correlation Spectroscopy (COSY) Introduction to NMR spectroscopy Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics I. NMR: the background Complex technique. Requires knowledge in: Mathematics Physics Chemistry Biology (Medicin) Involves a lot of computing. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy imaging. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a nuceli (Nuclear) specific spectroscopy that has far reaching applications throughout the physical sciences and industry. NMR uses a large (Magnetic) to probe the intrinsic spin properties of atomic nuclei. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Background Over the past fifty years nuclear resonance spectroscopy, commonly referred to as nmr, has become the preeminent technique for determining the structure of organic compounds. V Description Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy R. Abraham, School of Chemistry, University of Liverpool J. Fisher, Biological NMR Centre, University of Leicester P. Loftus, Stuart Pharmaceuticals, Delaware, USA This book is a new, extended edition of Proton. 3D NMR spectroscopy Each of the different indirect time periods (t1, t2) is incremented separately. Two categories of 3D experiments: Two 2D experiments in succession Introduction to NMR! nuclear resonance (NMR) spectroscopy Full Nobel prize in Chemistry for his development of nuclear resonance spectroscopy for determining the Spectroscopy is a general methodology that can be adapted in many ways to extract the information you need (energies of electronic, vibrational, rotational states, structure and symmetry of molecules, dynamic information). 1 An Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy A. The Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy nuclei with odd atomic number have a S with two spin states (12 and 12) The basic physical principles underlying proton NMR spectroscopy. The basic physical principles underlying proton NMR spectroscopy. The nucleus of a Hydrogen atom is a proton and has a property called spin. Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy Alternative sites exist that have an introduction to NMR theory. NMR webcourse from Queens Univ. Return to Index of sample NMR files. Return to Chemistry, UWIMona, Home Page. Page 2 NMR spectroscopy The energy difference between the state is proportional to the ratio of the nucleus and the magnitude of the applied field as shown in the figure and equation below. 2 Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy Labeling of this type is most easily accomplished biosynthetically in either E. coli or in tissue culture (at a much higher expense). A rough indication of the The WSU Center for NMR Spectroscopy is a central University facility that provides access to stateoftheart NMR instrumentation. NMR Spectroscopy A short Introduction Many Nuclei have an Inherent Angular Moment (or Spin) which is quantized and character ised by a spin quantum number Nuclear resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic methods used by chemists and biochemists to analyse the molecular and electronic structure of atoms and molecules. These are UVVisible, Infrared (IR) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopies. The content is presented using short. Introduction to nmr spectroscopy: r j abraham, j fisher, introduction to nmr spectroscopy r j abraham, school of chemistry, university of liverpool j fisher, biological nmr centre, university of leicester p loftus, stuart pharmaceuticals, delaware, usa this book is a new, extended edition of. Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy of Carbohydrates Johannes F. Vliegenthart Bijvoet Center, Department of Bioorganic Chemistry, Utrecht University, Padualaan 8, 3584 CH Utrecht, The Netherlands In this chapter an introductory overview is presented of A brief introduction to NMR spectroscopy of proteins By Flemming M. Introduction Nuclear resonance, NMR, and Xray crystallography are the only two methods that can be applied to the study of threedimensional molecular structures of proteins at atomic resolution. NMR spectroscopy is the only method that allows the He is a coauthor, with Donald L. Vyvyan of an organic spectroscopy book, INTRODUCTION TO SPECTROSCOPY, Fourth Edition (Cengage Learning). Professor Lampman also is the author of the computer program for teaching organic nomenclature: ORGANIC NOMENCLATURE: AN INTRODUCTION TO THE IUPAC SYSTEM. Powerpoint Templates Page 3 Introduction: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is a spectroscopy technique which is based on the absorption of radiation in the radio frequency region 4 to 900 MHz by nuclei of the atoms. Nuclear resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong static field are perturbed by a weak oscillating field (in the near field and therefore not involving waves) and respond by producing an signal with a frequency characteristic of the field at the nucleus. Nuclear resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is one of the most powerful and widely used techniques in chemical research for investigating structures and dynamics of molecules. Advanced methods can even be utilized for structure determinations of biopolymers, for example proteins or. Hornak is Professor of Chemistry and Imaging Science at the Rochester Institute of Technology where he teaches courses in resonance imaging, nuclear resonance spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and physical chemistry..






.jpg)
