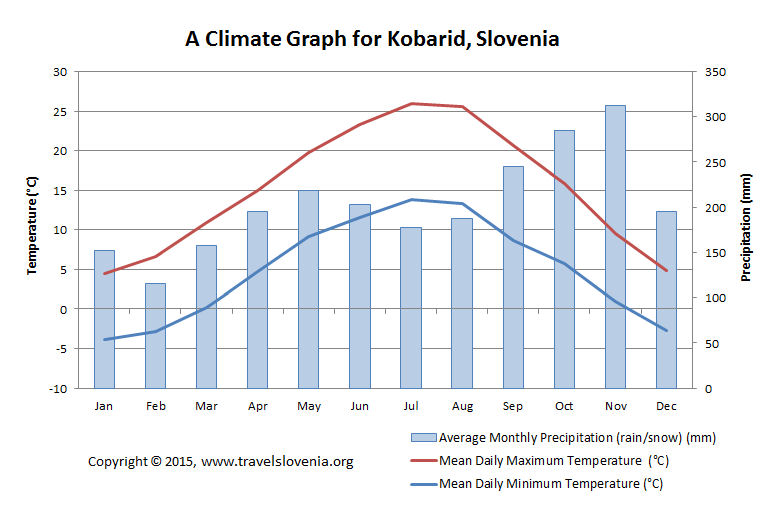
Introduction. This chapter summarizes how climate is changing, why it is changing, and what is projected for the future. While the focus is on changes in the United States, the need to provide context sometimes requires a broader geographical perspective. Climate meanwhile is defined as the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. It is the long term weather pattern of a given area. Before the end of June 2011, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) officially declared the year as being among the most extreme weatherevent years in recorded U. history (Morello ClimateWire, 2011). A guide to this section of the website. Introduction; History of Weather Forecasting; Articles in this Section; Introduction. This section of the website deals with the earth's atmosphere, and particulary with the science of meteorology. Meteorology has a theoretical aspect, a branch of classical physics. Introduction to China Climate In China, a vast land spanning many degrees of latitude with complicated terrain, climate varies radically. China has a variety of temperature and rainfall zones, including continental monsoon areas. Climate change is already causing significant impacts to people and ecosystems, and these impacts will grow much more severe in the coming years. We can choose to take economically sensible steps. Climate Summary for each student or group A copy of the Temperatures in the ontiguous 48 States, 1901 to 2011 graph Graph paper for each student Introduction to Weather. Meteorology is the study of weather. Weather is caused by the movement or transfer of energy. Energy is transferred wherever there is a temperature difference between two objects. Collage of pictures depicting different types of weather weather events. This course provides you with a practical introduction and overview of meteorology and climate. The nature of the physical processes responsible for changes in daily weather will be discussed, including links between oceans, atmosphere and land. Introduction to Climate Change. Climate is the longterm statistical expression of shortterm weather. Climate can be defined as expected weather. Watch videoWhere does climate stop and weather begin? And which is to blame when Mother Nature turns violent? Learn what makes nature unleash her fury and what you can do to protect yourself. Loaded with Canadian examples and extensive pedagogy, this text offers an engaging and relevant treatment of weather and climate to students in thiscountry. What people are saying Write a review We haven't found any reviews in the usual places. 1 Meteorology: an introduction to weather, climate and the environment by Dr John S. Reid Fellow of the Royal Meteorology Society Department of Physics Course introduces weather and climate. Topics include atmospheric processes, elements of weather, and a survey of world climates. Course may be offered in a facetoface or hybrid format. Course may be taught as facetoface, hybrid or online course. Required course practices are to be established. INTRODUCTION TO CLIMATE CHANGE: LECTURE NOTES FOR METEOROLOGISTS Prepared by 669 Workbook on numerical weather production for the tropics for the training of Class I and Class IImeteorological personnel. (EnglishSpanish) INTRODUCTION climate change. Description of the climate system and its components. The lapse rate is an important characteristic of the atmosphere. For instance, it determines its vertical stability. Introduction to Global Weather In the previous section, we have seen the sun as the source for our weather through the transfer of heat energy to the earth. The equatorial region receives the bulk of the heat energy but not always directly. Climate is the weather of a place averaged over a period of time, often 30 years. Climate information includes the statistical weather information that tells us about the normal weather, as well as the range of weather extremes for a location. Introduction to Weather and Climate Chapter Exam Instructions. Choose your answers to the questions and click 'Next' to see the next set of questions. You can skip questions if you would like and. Climate differs from weather, in that weather only describes the shortterm conditions of these variables in a given region. A region's climate is generated by the climate system, which has five components: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. METEOROLOGY TODAY: AN INTRODUCTION TO WEATHER, CLIMATE AND THE ENVIRONMENT by meteorologists C. Donald Ahrens and Robert Henson combines the latest in weather, climate and earth science to introduce students to the concepts and current issues of meteorology. Intro lesson to establish understanding of difference between weather and climate and methods of measurement and forecasting. geography ppt for weather and climate with detailed descriptions. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. Weather and climate are related but they differ in the time scales of changes and their predictability. They can be defined as follows. Weather is the instantaneous state of the atmosphere around us. Grounded in an interdisciplinary, systemsbased approach, Weather and Climate, provides an engaging, wellrounded introduction to the intricately intertwined processes that create weather and climate in Canada and around the globe. Climate change is at once the greatest challenge and the greatest opportunity humanity has ever faced. It is one that we can and must meet successfully to ensure our future. Introduction to Animated Videos The challenges in better understanding and adapting to the impact of climate change on water for the coming 50 years. The flows of water and sand in different riverine, coastal and ocean systems. How to identify mechanisms of climate change and explain the interplay of climate change, sea level, clouds, rainfall and future weather. Met Office weather forecasts for the UK. World leading weather services for the public. Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the lowest level of the atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to daytoday temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric. Did you know our videos are possible because of Patreon supporters! Join the community so we can make. As the world has warmed, that warming has triggered many other changes to the Earths climate. Changes in extreme weather and climate events, such as heat waves and droughts, are the primary way that most people experience climate change. Introduction to Weather and Climate Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives. This chapter starts off by defining weather and climate before delving into lessons on the major components and. Learn introduction to weather and climate with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 500 different sets of introduction to weather and climate flashcards on Quizlet. METEOROLOGY TODAY has for many years been one of the most widely used and authoritative texts for the introductory meteorology course. Each edition is extensively reviewed by leading researchers in the field to ensure that the text remains completely uptodate and reflects today's current understanding of meteorological concepts. Author Donald Ahrens has been widely praised for his ability to. New to weather or need a refresher? Start with this introduction to the basic principles and concepts of weather, meteorology, and the atmosphere. This website provides you with information about the weather and climate in almost every country around the world. Two of the most important factors determining climate are temperature and precipitation. Weather and Climate The Structure of the Atmosphere Surrounding the Earth is a gaseous envelope or atmosphere, held in place by the planets gravitational attraction. The Earths atmosphere is a complex dynamical, physical, and chemical system. Dynamic processes cover a The projected climate changes will influence both the energy requirements and the possibilities of energy production. Furthermore, extreme weather events could impact the planning, design and operation of. Introduction To Weather And Climate. Showing top 8 worksheets in the category Introduction To Weather And Climate. Some of the worksheets displayed are Weather and climate work, The weather classrooms elementary weather teacher guide, Introduction to geography, Second grade weather, E d t w w tm d, Weather and climate, Teaching pack for key stage 3, Swann house 22 william street. The year 2010 was the hottest year in Canada on record, with overall average temperatures three degrees warmer than average. We are living in a changing world and students have a growing interest in understanding global weather and climate patterns and their effect on our lives. Find helpful customer reviews and review ratings for Meteorology Today: An Introduction to Weather, Climate, and the Environment, 9th Edition at Amazon. Climate describes weather patterns at a place over a long period of time. Directions for This Lesson: In this lesson, you will learn the difference between weather and climate. First, try the practice questions to determine what you already know. What's the Difference Between Weather and Climate. A whole lesson introducing students to the topic of weather and climate. This includes all the resources for the lesson Introduction to Weather and Climate Before any conversation about weather or climate can begin, we need to begin with some astronomy and some physics. We need an understanding of our EarthSun relationship, how the relationship moderates energy, and what. This ability to mitigate or 'hedge' is especially useful for Wrms in sectors that are highly weather sensitive. Using an example from the energy sector, a highly weather sensitive sector, a Wrm. Rain or shine, learn how the weather works by exploring the science behind daily forecasts, weather safety, and climate change. Global climate is a description of the climate of a planet as a whole, with all the regional differences averaged. An El Nio Fish Tale Peruvian fishing boats used to return to shore each day heavy with anchovies, but in 1972 the boats returned to shore with empty nets..